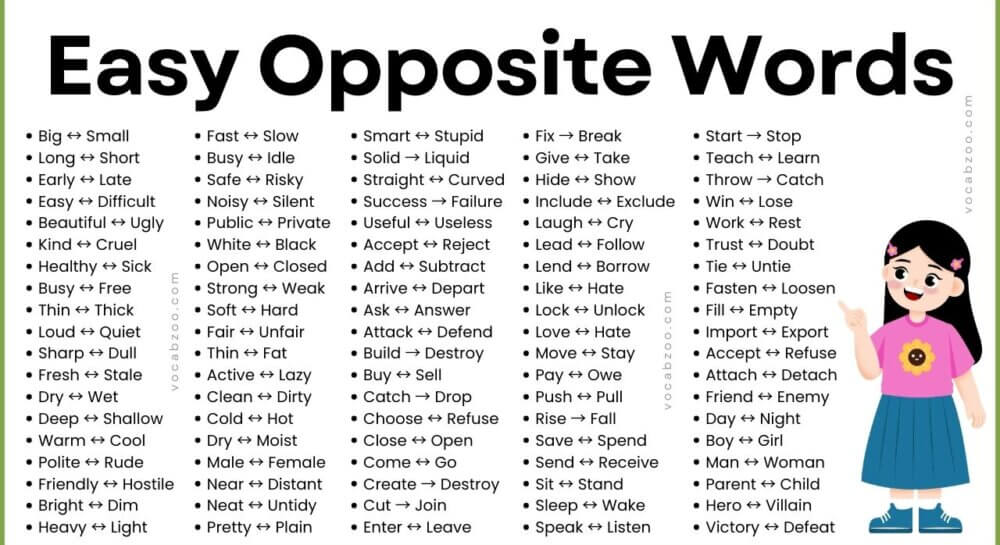
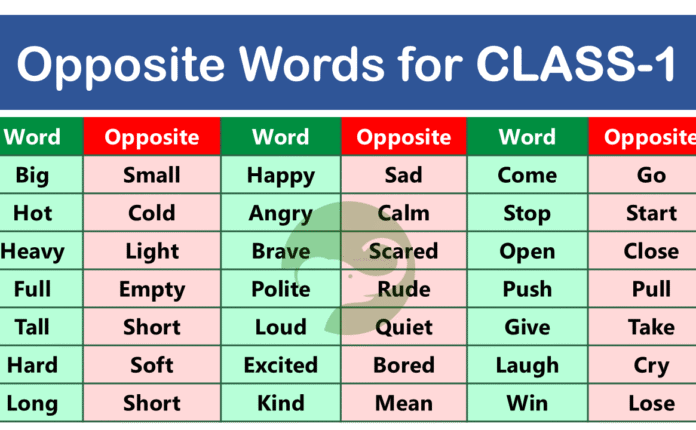
In this blog post, you will learn easy opposite word in English, build strong vocabulary, and clearly understand word meaning in daily English. Opposite words, also called antonyms, help English learners compare ideas, describe things better, and understand sentences with ease. These word pairs are used in speaking, reading, and writing at school and in daily life. By learning common opposite words, you can improve your understanding of English in a simple and practical way.
What Are Opposite Words?
Opposite words are called antonyms. These are words that have completely different meanings.
Examples:
- Big ↔ Small
- Hot ↔ Cold
- Fast ↔ Slow
They help us explain ideas in a clear and strong way.

Why Opposite Words Are Important
Opposite words help learners to:
- Speak clearly
- Write better sentences
- Understand meaning quickly
- Grow vocabulary fast
They are used in daily speaking, school lessons, writing, and exams.
Types of Opposite Words
Gradable Opposites
These show different levels.
Hot – Cold, Big – Small
Complementary Opposites
Only two choices.
Alive – Dead, Open – Closed
Relational Opposites
Show relationship.
Teacher – Student, Buy – Sell
Daily Use Opposite Words
| Word | Opposite | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Day | Night | I study at night. |
| Up | Down | Sit down please. |
| In | Out | Come inside. |
| Fast | Slow | He walks slowly. |
| Hot | Cold | The tea is cold. |
| Happy | Sad | She feels happy. |
| Near | Far | The shop is near. |
| Open | Close | Close the door. |
| Old | New | I bought a new bag. |
| Early | Late | He is late today. |
| Good | Bad | This is a good book. |
| High | Low | The price is low. |
| Clean | Dirty | Hands are dirty. |
| Hard | Soft | The pillow is soft. |
| Light | Dark | The room is dark. |
| Strong | Weak | He feels weak. |
| Rich | Poor | He is poor but kind. |
| Full | Empty | The bottle is empty. |
| Yes | No | She said no. |
| Start | End | The movie ends soon. |
| Buy | Sell | I sell fruits. |
| Give | Take | Take this book. |
| Push | Pull | Pull the door. |
| Laugh | Cry | The baby will cry. |
| Win | Lose | We lost the game. |
| On | Off | Turn off the light. |
| Tall | Short | The boy is tall. |
| Wide | Narrow | The road is narrow. |
| Begin | Finish | Finish your work. |
| Alive | Dead | The plant is dead. |
| Best | Worst | This is the worst day. |
| Bright | Dull | The colour is dull. |
| Careful | Careless | Drive carefully. |
| Cheap | Expensive | This phone is cheap. |
| Clear | Cloudy | The sky is cloudy. |
| Enter | Exit | Use this exit. |
| Few | Many | Many people came. |
| Forward | Backward | Step backward. |
| Like | Dislike | I dislike noise. |
| Lose | Find | I found my keys. |
| Quiet | Loud | The music is loud. |
| Safe | Dangerous | This road is dangerous. |
| Smooth | Rough | The road is rough. |
| Sweet | Sour | Lemon is sour. |
| Tidy | Messy | The room is messy. |
| True | False | That is false. |
| Wet | Dry | The clothes are dry. |
| Young | Old | The teacher is old. |
Adjective Opposites
- Big ↔ Small
- Long ↔ Short
- Early ↔ Late
- Easy ↔ Difficult
- Beautiful ↔ Ugly
- Kind ↔ Cruel
- Healthy ↔ Sick
- Brave ↔ Cowardly
- Busy ↔ Free
- Thin ↔ Thick
- Loud ↔ Quiet
- Sharp ↔ Dull
- Fresh ↔ Stale
- Dry ↔ Wet
- Deep ↔ Shallow
- Warm ↔ Cool
- Polite ↔ Rude
- Honest ↔ Dishonest
- Friendly ↔ Hostile
- Bright ↔ Dim
- Heavy ↔ Light
- Fast ↔ Slow
- Busy ↔ Idle
- Safe ↔ Risky
- Noisy ↔ Silent
- Public ↔ Private
- Simple ↔ Complex
- Strong ↔ Weak
- Soft ↔ Hard
- Fair ↔ Unfair
- Thin ↔ Fat
- Active ↔ Lazy
- Clean ↔ Dirty
- Cold ↔ Hot
- Dry ↔ Moist
- Male ↔ Female
- Modern ↔ Traditional
- Near ↔ Distant
- Neat ↔ Untidy
- Permanent → Temporary
- Positive ↔ Negative
- Pretty ↔ Plain
- Smart ↔ Stupid
- Solid → Liquid
- Straight ↔ Curved
- Success → Failure
- Useful ↔ Useless
- White ↔ Black
- Open ↔ Closed
Verb Opposites
- Accept ↔ Reject
- Add ↔ Subtract
- Arrive ↔ Depart
- Ask ↔ Answer
- Attack ↔ Defend
- Build → Destroy
- Buy ↔ Sell
- Catch → Drop
- Choose ↔ Refuse
- Close ↔ Open
- Come ↔ Go
- Create → Destroy
- Cut → Join
- Enter ↔ Leave
- Fix → Break
- Give ↔ Take
- Hide ↔ Show
- Increase ↔ Decrease
- Include ↔ Exclude
- Laugh ↔ Cry
- Lead ↔ Follow
- Lend ↔ Borrow
- Like ↔ Hate
- Lock ↔ Unlock
- Love ↔ Hate
- Move ↔ Stay
- Pay ↔ Owe
- Push ↔ Pull
- Remember ↔ Forget
- Rise → Fall
- Save ↔ Spend
- Send ↔ Receive
- Sit ↔ Stand
- Sleep ↔ Wake
- Speak ↔ Listen
- Start → Stop
- Teach ↔ Learn
- Throw → Catch
- Win ↔ Lose
- Work ↔ Rest
- Zoom In ↔ Zoom Out
- Trust ↔ Doubt
- Tie ↔ Untie
- Fasten ↔ Loosen
- Fill ↔ Empty
- Import ↔ Export
- Repair → Damage
- Accept ↔ Refuse
- Attach ↔ Detach
- Advance ↔ Retreat
Noun Opposites
- Friend ↔ Enemy
- Teacher ↔ Student
- Day ↔ Night
- Boy ↔ Girl
- Man ↔ Woman
- Parent ↔ Child
- Leader ↔ Follower
- Hero ↔ Villain
- Victory ↔ Defeat
- Truth ↔ Lie
- Beginning → End
- Noise ↔ Silence
- Love ↔ Hate
- Luck ↔ Misfortune
- Peace ↔ War
- Profit ↔ Loss
- Health ↔ Illness
- Work ↔ Holiday
- Riches ↔ Poverty
- Order ↔ Chaos
- Front ↔ Back
- Inside ↔ Outside
- Top ↔ Bottom
- East ↔ West
- North ↔ South
- Life → Death
- Success ↔ Failure
- Entrance ↔ Exit
- Friendship ↔ Rivalry
- Strength ↔ Weakness
- Freedom ↔ Control
- Hope ↔ Despair
- Joy ↔ Sorrow
- Right ↔ Left
- Morning ↔ Evening
- Wisdom ↔ Foolishness
- Comfort ↔ Pain
- Safety ↔ Danger
- Credit ↔ Debt
- Employer ↔ Employee
- Guest ↔ Host
- Buyer ↔ Seller
- Winner ↔ Loser
- Heaven ↔ Hell
- Fact ↔ Fiction
- Majority ↔ Minority
- Public ↔ Private
- Arrival → Departure
- Ally ↔ Opponent
- Cause → Effect
Direction, Time & Place Opposites
- Above ↔ Below
- Before ↔ After
- Here ↔ There
- Left ↔ Right
- Near ↔ Far
- Inside ↔ Outside
- Upstairs ↔ Downstairs
- North ↔ South
- East ↔ West
- Now ↔ Then
- Past ↔ Future
- Early ↔ Late
- Open ↔ Closed
- Arrival ↔ Departure
- Inland ↔ Coastal
- Urban ↔ Rural
- Visible ↔ Hidden
- Top ↔ Bottom
- Short-term ↔ Long-term
- Public ↔ Private
- Daytime ↔ Night-time
- Right side ↔ Wrong side
- Entry ↔ Exit
- Present ↔ Absent
- Near side ↔ Far side
- Foreground ↔ Background
- Centre ↔ Edge
- Horizontal ↔ Vertical
- Arrival ↔ Leave
- Fast track ↔ Slow track
Personality & Feeling Opposites
- Happy ↔ Sad
- Confident ↔ Nervous
- Kind ↔ Mean
- Brave ↔ Afraid
- Calm ↔ Angry
- Patient ↔ Impatient
- Honest ↔ Dishonest
- Friendly ↔ Unfriendly
- Positive ↔ Negative
- Proud ↔ Ashamed
- Relaxed ↔ Stressed
- Hopeful ↔ Hopeless
- Excited ↔ Bored
- Caring ↔ Selfish
- Polite ↔ Rude
- Cheerful ↔ Gloomy
- Quiet ↔ Talkative
- Trusting ↔ Suspicious
- Serious ↔ Playful
- Warm ↔ Cold
- Strong ↔ Weak
- Bold ↔ Shy
- Loyal ↔ Disloyal
- Active ↔ Lazy
- Optimistic ↔ Pessimistic
- Fair ↔ Biased
- Gentle ↔ Rough
- Secure ↔ Insecure
- Helpful ↔ Harmful
- Wise ↔ Foolish
- Tolerant ↔ Intolerant
- Relaxed ↔ Tense
- Stable ↔ Unstable
- Bright ↔ Dull
- Free ↔ Trapped
Easy Opposite Words for Kids
Big ↔ Small
Meaning: Big means large, small means little.
Example: The big elephant sat near the small mouse.
Hot ↔ Cold
Meaning: Hot means very warm, cold means very cool.
Example: The tea is hot, but the water is cold.
Fast ↔ Slow
Meaning: Fast means quick, slow means not quick.
Example: The rabbit is fast, but the turtle is slow.
Happy ↔ Sad
Meaning: Happy means glad, sad means not happy.
Example: She feels happy when she wins and sad when she loses.
Up ↔ Down
Meaning: Up means above, down means below.
Example: The ball went up and then came down.
Open ↔ Closed
Meaning: Open means not shut, closed means shut.
Example: The shop is open in the day and closed at night.
Day ↔ Night
Meaning: Day is light time, night is dark time.
Example: I go to school in the day and sleep at night.
Clean ↔ Dirty
Meaning: Clean means not dirty, dirty means not clean.
Example: My hands are dirty, so I will make them clean.
Full ↔ Empty
Meaning: Full means nothing can fit more, empty means nothing is inside.
Example: The glass is full of milk, the cup is empty.
Near ↔ Far
Meaning: Near means close, far means at a long distance.
Example: My school is near, but the park is far.
Tall ↔ Short
Meaning: Tall means high, short means not tall.
Example: The tall boy stood next to the short girl.
Good ↔ Bad
Meaning: Good means nice, bad means not nice.
Example: This is a good habit, not a bad one.
Laugh ↔ Cry
Meaning: Laugh means to be happy, cry means to be sad.
Example: The baby will laugh when happy and cry when hungry.
Light ↔ Dark
Meaning: Light means bright, dark means not bright.
Example: The room is dark, please turn on the light.
Soft ↔ Hard
Meaning: Soft means easy to press, hard means not soft.
Example: The pillow is soft, the table is hard.
Yes ↔ No
Meaning: Yes means agree, no means not agree.
Example: I said yes to the game and no to the toy.
In ↔ Out
Meaning: In means inside, out means outside.
Example: The cat is in the house, the dog is out.
Strong ↔ Weak
Meaning: Strong means having power, weak means having little power.
Example: The hero is strong, but the boy feels weak.
Wet ↔ Dry
Meaning: Wet means full of water, dry means no water.
Example: My clothes are wet in rain and dry in the sun.
Early ↔ Late
Meaning: Early means before time, late means after time.
Example: I wake up early, but my brother wakes up late.
Push ↔ Pull
Meaning: Push means press forward, pull means draw towards you.
Example: Please push the door, don’t pull it.
Buy ↔ Sell
Meaning: Buy means to get with money, sell means to give for money.
Example: I buy fruit, the shopkeeper sells fruit.
Win ↔ Lose
Meaning: Win means to succeed, lose means not succeed.
Example: One team will win, the other will lose.
Kind ↔ Mean
Meaning: Kind means caring, mean means unkind.
Example: A kind child helps others, a mean child hurts others.
Start ↔ End
Meaning: Start means to begin, end means to finish.
Example: The class starts at 9 and ends at 2.

Learning Tips
- Learn 5 to 10 opposites daily
- Use them in your own sentences
- Read them aloud for speaking practice
- Match words with daily life situations
Learning opposite words in English is one of the smartest and quickest ways to grow your vocabulary. These 250+ easy opposites with examples will help you speak better, write clearly, and understand English faster. Keep practising daily and your confidence will grow naturally.
Opposite Words PDF
FAQs about Easy Opposite Word in English
What are opposite words in English?
Opposite words are words that have completely different meanings, such as big–small, hot–cold, and happy–sad. They help us understand ideas more clearly.
Why are opposite words important for kids?
Opposite words help children improve vocabulary, understand meanings faster, and speak and write English more clearly in daily life and schoolwork.
What is the opposite word of big?
The opposite word of big is small.
Example: The big box is next to the small box.
What is the opposite of happy in English?
The opposite of happy is sad.
Example: She feels happy today but was sad yesterday.
What is the opposite word of fast?
The opposite of fast is slow.
Example: The car is fast, but the bicycle is slow.
What is the opposite of hot?
The opposite of hot is cold.
Example: The soup is hot, but the juice is cold.
What is the opposite of day?
The opposite of day is night.
Example: We play in the day and sleep at night.
What is the difference between open and closed?
Open means not shut, and closed means shut.
Example: The door is open now but will be closed later.
How many types of opposite words are there?
There are mainly three types: gradable opposites (hot–cold), complementary opposites (open–closed), and relational opposites (teacher–student).
How can kids learn opposite words easily?
Kids can learn opposite words by using them in daily sentences, reading them aloud, matching word pairs, and practising with simple examples every day.
Read More