Future tenses help us talk about actions or events that will happen later. In English, there are four main types of future tenses, and each one has its own way of showing time. In this blog post, you will learn their simple definitions, structures, examples, usage, and time words to help you speak and write about the future correctly.
All are explained shortly with easy examples, so you can easily memorize how to talk about future actions and decisions. In this blog post, you will build simple and clear knowledge of future tenses to make your English stronger and more correct. Let’s begin with today’s lesson!
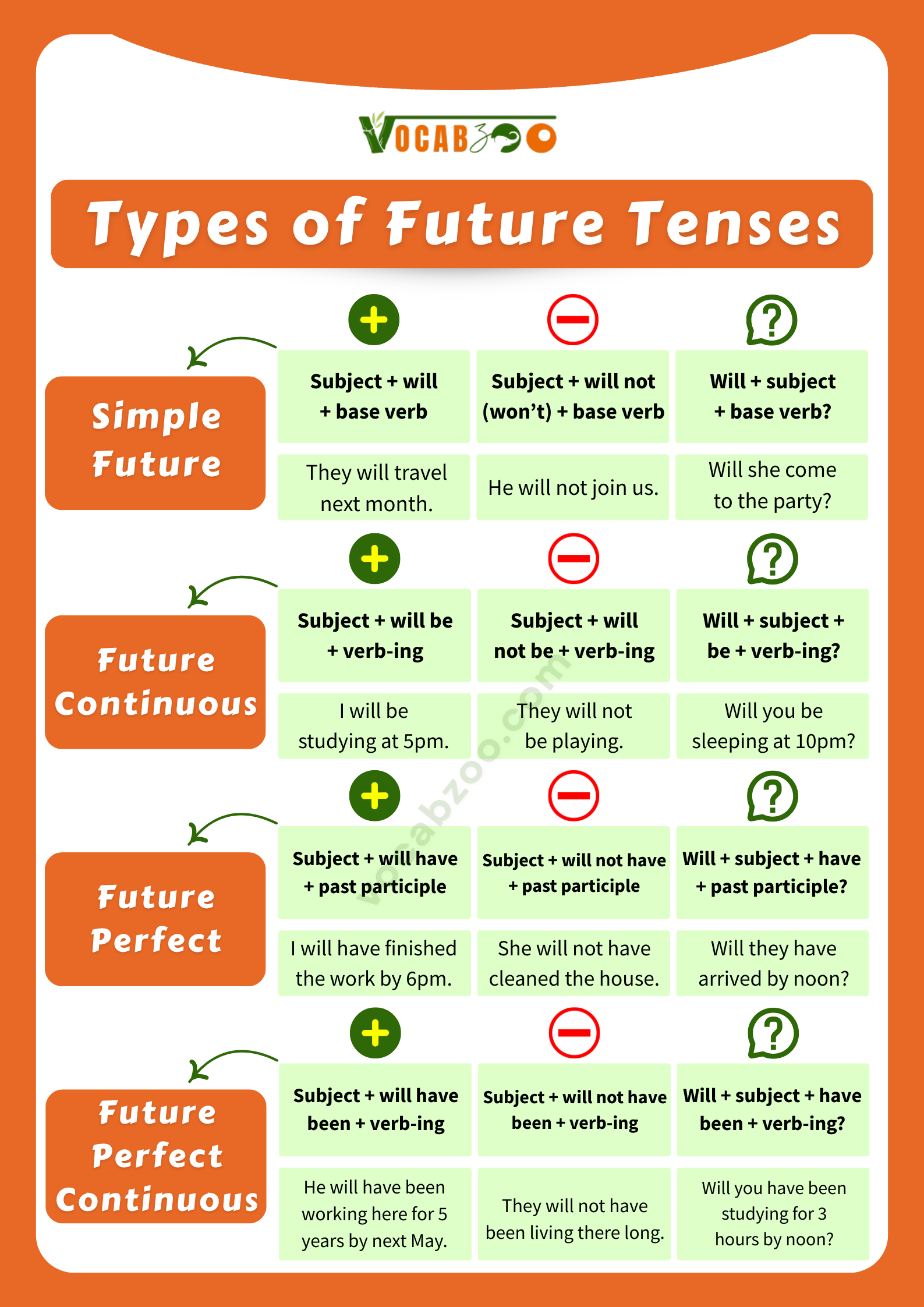
1. Simple Future Tense
The simple future tense talks about actions that will happen later or decisions made at the moment of speaking.
Structure of Simple Future:
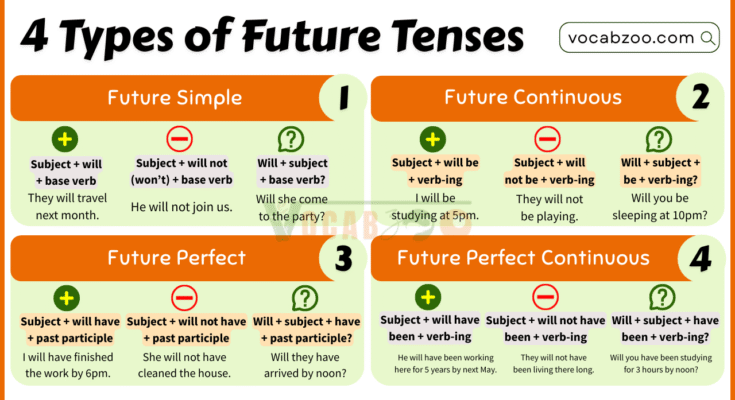
Positive: Subject + will + base verb
I will go to school.
Negative: Subject + will not (won’t) + base verb
She will not play tennis.
Question: Will + subject + base verb?
Will you help me?
Usage of Simple Future:
Decisions made right now
Example: I will answer the phone.
Predictions
Example: It will rain tomorrow.
Offers or promises
Example: I will help you with your homework.
Examples of Simple Future:
| Form | Example |
|---|---|
| Positive | They will travel next month. |
| Negative | He will not join us. |
| Question | Will she come to the party? |
Time Words Used in the Simple Future:
- tomorrow
- next week
- in a few days
- soon
2. Future Continuous (Progressive) Tense
The future continuous tense talks about an action that will be happening at a certain time in the future.
Structure of Future Continuous Tense:
Positive: Subject + will be + verb-ing
I will be studying at 5pm.
Negative: Subject + will not be + verb-ing
They will not be playing.
Question: Will + subject + be + verb-ing?
Will you be sleeping at 10pm?
Usage of Future Continuous Tense:
An action in progress in the future
Example: At this time tomorrow, I will be traveling.
To ask politely about plans
Example: Will you be using the car tonight?
Examples of Future Continuous Tense:
| Form | Example |
|---|---|
| Positive | She will be working all day. |
| Negative | We will not be waiting. |
| Question | Will they be coming with us? |
Time Words Used in the Future Continuous Tense:
- at this time tomorrow
- next week at [time]
- in the morning/afternoon/evening
3. Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense talks about something that will be finished before a certain time in the future.
Structure of Future Perfect Tense:
Positive: Subject + will have + past participle
I will have finished the work by 6pm.
Negative: Subject + will not have + past participle
She will not have cleaned the house.
Question: Will + subject + have + past participle?
Will they have arrived by noon?
Usage of Future Perfect Tense:
To show an action will be complete before another future action or time
Example: By next month, he will have saved enough money.
Examples of Future Perfect Tense:
| Form | Example |
|---|---|
| Positive | They will have left by 8pm. |
| Negative | I will not have finished my homework. |
| Question | Will you have cooked dinner before they come? |
Time Words Used in the Future Perfect Tense:
- by tomorrow
- by next week
- before [time]
4. Future Perfect Continuous (Progressive) Tense
The future perfect continuous tense shows that an action will continue up to a point in the future.
Structure of Future Perfect Continuous:
Positive: Subject + will have been + verb-ing
He will have been working here for 5 years by next May.
Negative: Subject + will not have been + verb-ing
They will not have been living there long.
Question: Will + subject + have been + verb-ing?
Will you have been studying for 3 hours by noon?
Usage of Future Perfect Continuous:
To show the duration of an action up to a certain future time
Example: Next year, I will have been teaching for 10 years.
Examples of Future Perfect Continuous:
| Form | Example |
|---|---|
| Positive | She will have been waiting for an hour by the time we arrive. |
| Negative | He will not have been driving for long. |
| Question | Will they have been working there for 5 years? |
Time Words Used in the Future Perfect Continuous:
- for [duration]
- by [time]
- before [future time]
Future Tenses Chart
| Tense | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Future | will + base verb | I will call you. |
| Future Continuous | will be + verb-ing | She will be studying. |
| Future Perfect | will have + past participle | They will have finished. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | will have been + verb-ing | He will have been working. |
Time Words Summary for Future Tenses
Simple Future: tomorrow, soon, next month
Future Continuous: at 5pm tomorrow, next week at 9am
Future Perfect: by Monday, before next year
Future Perfect Continuous: for 3 years, by the end of June
Quick Tips to Remember
Simple Future: use will for predictions or quick decisions
Future Continuous: use will be + verb-ing for actions in progress
Future Perfect: use will have + past participle for finished actions
Future Perfect Continuous: use will have been + verb-ing to show duration
Read More
This explanation of the four types of future tenses is so clear and easy to follow! The examples really help me see how to use each tense correctly in sentences. Thanks for making English grammar simpler and more understandable with this helpful guide!