In this blog post, you will learn the types of verbs in easy wording. Verbs are action or state words that help you build clear sentences. With short examples, you will understand how each type works, so you can speak and write better English with confidence.
What are Verbs?
A verb is a word that shows action or state of being.
It tells what someone or something does.
- Ali runs fast.
- She is happy.
So, a verb tells us what is happening in a sentence.
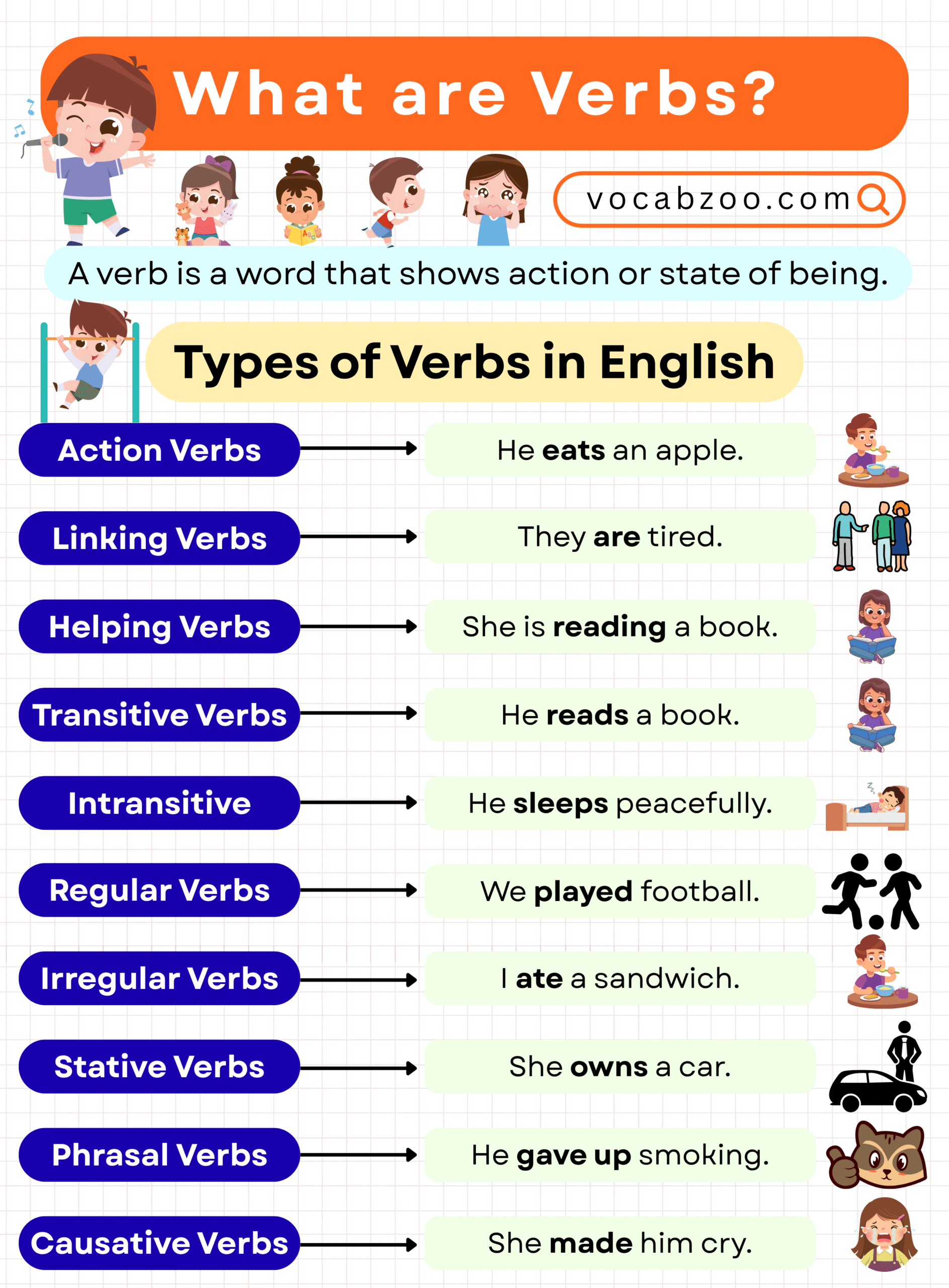
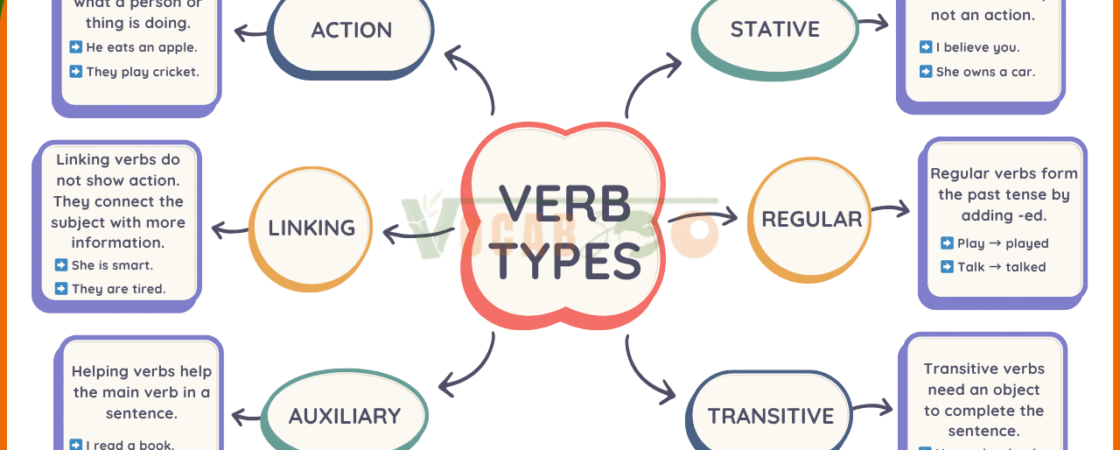
Types of Verbs in English
Let’s learn the main types of verbs one by one with easy meanings and examples.
Action Verbs
Action verbs show what a person or thing is doing.
Examples:
- He eats an apple.
- They play cricket.
- I write a letter.
Easy Tip: If you can do it, it’s an action verb.
Linking Verbs
Linking verbs do not show action. They connect the subject with more information.
Common linking verbs: is, am, are, was, were, be, been, being
Examples:
- She is smart.
- They are tired.
- It was a great day.
Easy Tip: If the verb tells what something is, then it’s a linking verb.
Helping Verbs (Auxiliary Verbs)
Helping verbs help the main verb in a sentence.
Common helping verbs: is, am, are, was, were, have, has, had, will, shall, can, could, would, should
Examples:
- She is reading a book.
- I have finished my work.
- We will go tomorrow.
Easy Tip: If the verb comes before the action, it is a helping verb.
Transitive Verbs
Transitive verbs need an object to complete the sentence.
Examples:
- He reads a book.
- She watches TV.
Object is needed after the verb.
Intransitive Verbs
Intransitive verbs do not need an object.
Examples:
- He sleeps peacefully.
- They arrived late.
No object is used.
Regular Verbs
Regular verbs form the past tense by adding -ed.
Examples:
| Base Verb | Past Tense | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| play | played | We played football. |
| clean | cleaned | She cleaned her room. |
| talk | talked | I talked to my friend. |
| watch | watched | They watched a movie. |
| walk | walked | He walked to school. |
Note: Regular verbs make their past tense by simply adding -ed.
Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs do not follow the -ed rule.
Examples:
| Base Verb | Past Tense | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| go | went | She went to the market. |
| eat | ate | I ate a sandwich. |
| take | took | He took my pen. |
| see | saw | We saw a rainbow. |
| come | came | They came early. |
Note: Irregular verbs do not follow the -ed rule. Their past forms are different and must be memorized.
Stative Verbs
These verbs describe a state, not an action. They usually talk about feelings, thoughts, possession, or senses.
Examples:
- I believe you.
- She owns a car.
- This cake tastes good.
Tip: Stative verbs are not usually used in continuous tense.
Dynamic Verbs
These are the opposite of stative verbs. They show real actions or movements.
Examples:
- He runs every morning.
- They build houses.
Most action verbs are
Phrasal Verbs
A phrasal verb is made by combining a verb + preposition/adverb. The meaning is often different from the original verb.
Examples:
- He gave up smoking.
- She looks after her baby.
Tip: You must learn them as phrases because meaning often changes completely.
Causative Verbs
These verbs show that one person causes another to do something. Common causative verbs are make, let, have, get.
Examples:
- She made him cry.
- I got my car washed.
- They let him go.
Modal Verbs (also called Modal Auxiliaries)
Modal verbs show possibility, permission, ability, or necessity.
Common modals: can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would
- You should study.
- She can swim.
- We might go later.
They are always used with base form of verb (without “to”).
Verb Types Summary
| Verb Type | Meaning / Use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Action | Shows real action | He runs fast. |
| Linking | Shows state or connection | She is tired. |
| Helping | Supports the main verb | They are going. |
| Transitive | Needs an object | I read a book. |
| Intransitive | No object needed | She cried loudly. |
| Regular | Past = Verb + ed | We played well. |
| Irregular | Past = Different form | He went home. |
| Stative | Describes state or feeling | I love pizza. |
| Dynamic | Describes real action | He runs daily. |
| Phrasal | Verb + preposition/adverb | She gave up early. |
| Causative | One causes another to act | I had him fix it. |
| Modal | Shows mood/ability/necessity | You must learn this. |
Easy Practice
Find the verb in these sentences:
- The cat sleeps on the sofa.
- She is reading a novel.
- I played football yesterday.
- They were happy.
- He goes to school.
Answers:
-
sleeps | 2. is reading | 3. played | 4. were | 5. goes
FAQs
Q1: What is the most common verb in English?
A: The verb “be” (is, am, are) is the most common.
Q2: How can I know the type of a verb?
A: Look at what the verb is doing. Is it showing action? Is it helping? Is it connecting? That tells you the type.
Q3: Can a verb be both helping and action?
A: Yes, for example: She is running. → “is” = helping, “running” = action.
Read More